Room ORM
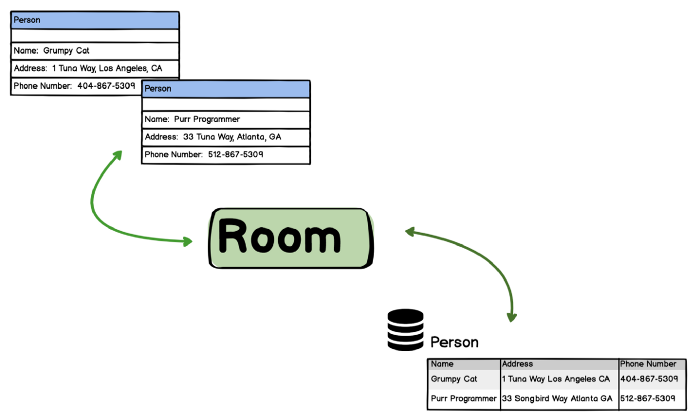
Android ROOM is an abstraction layer over SQLite. An Android ROOM introduced in Google I/O 2017. Android ROOM implements ORM (Object — Relational Mapping) to store data.
So, What is ORM?
Object-relational mapping (ORM, O/RM, and O/R mapping) is a programming technique for converting data between incompatible type systems in relational databases and object-oriented programming languages. This creates, in effect, a “virtual object database” that can be used from within the programming language.Wikipedia reference:-
Advantages of an Android ROOM:-
- ROOM provides compile-time verification of SQL Queries.
- ROOM will update SQL queries as schema changes.
- ROOM will work with LiveData and RxJava.
To implement ORM in an Android, following are the famous libraries available.
1) Sugar ORM
2) GreenDAO
3) Realm
4) ORM Lite
5) ROOM.
Implementation:
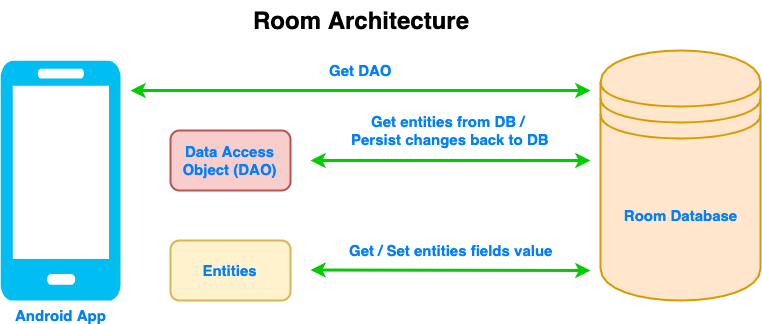
The three major components of Android Room are:
- Entity: Represents a table within the Room Database. It should be annotated with @Entity.
- DAO: An interface that contains the methods to access the database. It is annotated with @Dao.
- Database: Represents the database. It’s an object that holds a connection to the SQLite database, and all the operations are executed through it. It is annotated with @Database.
Dependencies
// Navigation Component implementation 'androidx.navigation:navigation-fragment-ktx:2.5.2' implementation 'androidx.navigation:navigation-ui-ktx:2.5.2' // Room components implementation "androidx.room:room-runtime:2.4.3" kapt "androidx.room:room-compiler:2.4.3" implementation "androidx.room:room-ktx:2.4.3" androidTestImplementation "androidx.room:room-testing:2.4.3" // Lifecycle components implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-extensions:2.2.0" implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-common-java8:2.5.1" implementation "androidx.lifecycle:lifecycle-viewmodel-ktx:2.5.1" // Kotlin components implementation "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib-jdk7:1.7.10" api "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.3.8" api "org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-android:1.6.1"
Dependencies 2 (if failed to sync)
Apply plugin if it failed to sync.
apply plugin: 'com.android.application' apply plugin: 'kotlin-android' apply plugin: 'kotlin-android-extensions' apply plugin: 'kotlin-kapt' android { //.. Omitted since it is not relevant for the example } dependencies { //... some dependencies were omitted due to they are not relevant for the example def room_version = "2.2.0-rc01" implementation "androidx.room:room-runtime:$room_version" kapt "androidx.room:room-compiler:$room_version" compile 'com.google.code.gson:gson:2.2.4' implementation 'io.reactivex.rxjava2:rxandroid:2.0.2' implementation 'io.reactivex.rxjava2:rxjava:2.1.17'
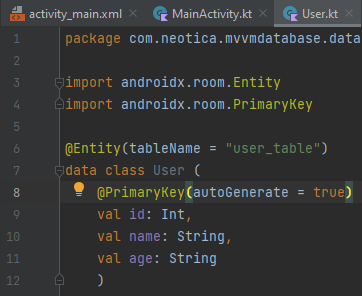
Step 1: Create Entity Class
In our project, User.kt is the Entity class.
Step 2: Create DAO Interface
In our project, UserDAO.kt is the DAO Interface.
DAO Interface Properties
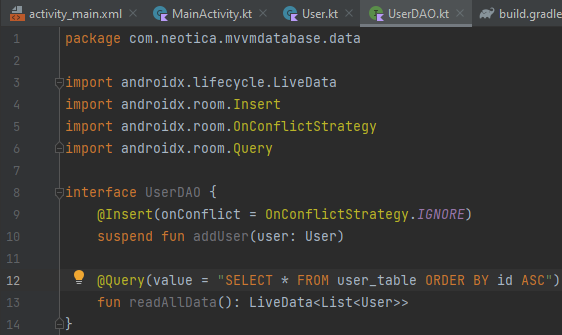
DAO Interface sample. @Insert(onConflict = OnConflinctStrategy.IGNORE) is used to ignore other class name that might be conflicting with the name of current class name that are currently being used.
Meanwhile @Query(value = “SELECT * FROM user_table ORDER BY id ASC”) is similar to how ORDER BY works in SQLITE.
Step 3: Create Database Class
Database contains the database holder and serves as the main access point for the underlying connection to the app’s persisted, relational data.
In our project, UserDatabase is the Database class.
Database class attributes and properties.
Make the class abstract by adding ‘abstract’ keyword in front of the class, and we will extend it to RoomDatabase. Don’t forget to annotate it.
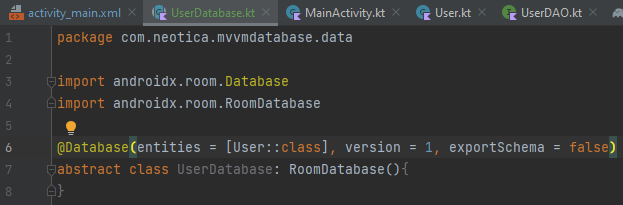
In the Annotation, we could see several perimeters. Which are:
- Entities: Our entity class, which in this case is User.kt
- Version: The version of our database
- ExportSchema: Basically to make records of the database version. Might be related to version control (Git) must research more later.
Step 4: Create a UserDAO abstract function.
We are going to create an abstract function that will return the UserDAO Class.
abstract fun userDao: UserDAOFull Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data import androidx.room.Database import androidx.room.RoomDatabase @Database(entities = (User::class), version = 1, exportSchema = false) abstract class UserDatabase: RoomDatabase(){ abstract fun userDAO: UserDAO }
Step 5: Create a Companion Object.
companion object{}Full Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data import androidx.room.Database import androidx.room.RoomDatabase @Database(entities = (User::class), version = 1, exportSchema = false) abstract class UserDatabase: RoomDatabase(){ abstract fun userDAO: UserDAO companion object{} }
As quoted from the Objects and Companion Page:
A companion objects is written within any class. And also, everything that is written inside the companion object will be basically visible to other classes.
companion object{}Full Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data import androidx.room.Database import androidx.room.RoomDatabase @Database(entities = (User::class), version = 1, exportSchema = false) abstract class UserDatabase: RoomDatabase(){ abstract fun userDAO: UserDAO companion object{} }
Step 6: Making INSTANCE.
We are going to make our class as a singleton. A singleton class will only have one instance. But we will make the initial value for our instance variable as zero, thus null.
companion object{
private var INSTANCE: UserDatabase? = null
}Full Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data import androidx.room.Database import androidx.room.RoomDatabase @Database(entities = (User::class), version = 1, exportSchema = false) abstract class UserDatabase: RoomDatabase(){ abstract fun userDAO(): UserDAO companion object{ private var INSTANCE: UserDatabase? = null } }
Step 7: Add Volatile Annotation.
Inside the companion object, we must add @Volatile annotation. Volatile make the rights to this field, immediately made visible to other threads.
companion object{
@Volatile
private var INSTANCE: UserDatabase? = null
}Full Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data import androidx.room.Database import androidx.room.RoomDatabase @Database(entities = (User::class), version = 1, exportSchema = false) abstract class UserDatabase(): RoomDatabase(){ abstract fun userDAO: UserDAO companion object{ @Volatile private var INSTANCE: UserDatabase? = null } }
Step 8: Create getDatabase function.
Then we are going to make a getDatabase function below it.
Code
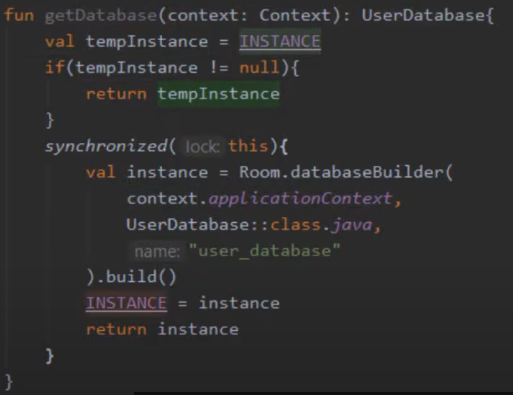
fun getDatabase(context: Context): UserDatabase{ val tempInstance = INSTANCE if(tempInstance != null){ return tempInstance } synchronized( this){ val instance = Room.databaseBuilder( context.applicationContext, UserDatabase::class.java, "user_database" ).build() INSTANCE = instance return instance } }
Full Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data import androidx.room.Database import androidx.room.RoomDatabase @Database(entities = (User::class), version = 1, exportSchema = false) abstract class UserDatabase: RoomDatabase(){ abstract fun userDAO(): UserDAO companion object{ @Volatile private var INSTANCE: UserDatabase? = null fun getDatabase(context: Context): UserDatabase{ val tempInstance = INSTANCE if(tempInstance != null){ return tempInstance } synchronized( this){ val instance = Room.databaseBuilder( context.applicationContext, UserDatabase::class.java, "user_database" ).build() INSTANCE = instance return instance } } } }
Step 9: Create Repository
A Repository abstracts access to multiple data sources.
The repository is not part of the architecture components, but it is a suggested practice for code separation and clean architecture.
Add a perimeter of the class to the DAO.
Code
class UserRepository (private val userDAO: UserDAO){ }
Full Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data class UserRepository (private val userDAO: UserDAO){}
Step 9.1: Create variable readAllData. This variable will list all the users wrapped inside the livedata object. We are going to read the data from this user DAO.
Code
val readAllData: LiveData<List<User>> = userDAO.readAllData()
Full Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data import androidx.lifecycle.LiveData class UserRepository (private val userDAO: UserDAO){ val readAllData: LiveData<List<User>> = userDAO.readAllData() }
Step 9.2: Create addUser function to add the user.
Use the DAO to access our addUser function from our userDAO.
And the function will have a suspend keyword since we are going to use coroutines in a viewmodel.
Code
suspend fun addUser(user: User){ userDAO.addUser(user)
Full Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data import androidx.lifecycle.LiveData class UserRepository (private val userDAO: UserDAO){ val readAllData: LiveData<List<User>> = userDAO.readAllData() suspend fun addUser(user: User){ userDAO.addUser(user) } }
Step 10: Create ViewModel.
Heres an explanation of the ViewModel: ViewModel.
Create a ViewModel Class.
Step 10.1: Extends to AndroidViewModel.
Extends the ViewModel class to AndroidViewModel, a dependency from Android Lifecycle.
Android ViewModel is different from regular ViewModel since it contains application reference.
Code
class UserViewModel: AndroidViewModel { }
Full Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data import androidx.lifecycle.AndroidViewModel class UserViewModel: AndroidViewModel { }
Step 10.2: Add the Application Reference.
Code
class UserViewModel(application: Application): AndroidViewModel(application) { }
Full Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data import android.app.Application import androidx.lifecycle.AndroidViewModel class UserViewModel(application: Application): AndroidViewModel(application) { }
Step 10.3: Create a variable named readAllData.
Create the variable inside the userViewModel class The readAllData will contains the lists of users, wrapped in the LiveData object.
Code
private val readAllData: LiveData<List<User>>
Full Code
package com.neotica.mvvmdatabase.data import android.app.Application import androidx.lifecycle.AndroidViewModel import androidx.lifecycle.LiveData class UserViewModel(application: Application): AndroidViewModel(application) { private val readAllData: LiveData<List<User>> }
Step 10.4: Create init block.
Init block is always first executed when the user ViewModel is called.
Reference:

 https://gorillalogic.com/blog/android-room-tutorial-simplifying-how-you-work-with-app-data/
https://gorillalogic.com/blog/android-room-tutorial-simplifying-how-you-work-with-app-data/